Robotics: The future of innovation

By Mamata Saha
Introduction: What does the term ‘Robotics’ mean?
Robotics is a field of study that blends science, engineering, and technology, and is dedicated to creating robots, which are essentially machines, to perform human tasks. Processes such as conception, design, manufacturing, and operation make up the field. If we consider the scenario as it existed around 17 years ago, robots were built for more mechanical and mundane tasks such as assembling car parts and other similar tasks.
At the same time, if technology has advanced by leaps and bounds in all these years, Robotics and robots have too. So, how far has Robotics progressed till now? Not so surprisingly, today we’re looking at building robots for tasks that are more intellectually challenging such as ensuring law and order, performing surgeries, and identifying landmines in war zones!
Origin and history: Robotics
The word ‘robot’ originated from the Czech word ‘robota,’ which stands for ‘forced labor.’ In the 1920 play titled ‘R.U.R’ (Rossum’s Universal Robots), Czech writer Karel Capek used instances of the word to hint at the characters of the play that comprised mass-produced characters not equipped with the ability to think. Interestingly, Oxford Dictionary gives credit to Isaac Asimov, the science fiction writer, for being the first person to use the word. Asimov’s contribution to the world of Robotics doesn’t end here. He went ahead and coined the three core laws that are imperative to the functioning of smart machines and autonomous robots, such as the following:
- Robots will not cause any harm to human beings.
- Robots must adhere to the instructions given by humans without hurting them.
- Robots need to ensure their own protection, but not at the cost of other rule violations.
While there have been several developments throughout the 60s, 70s, 80s, 90s, and 2000s, all the way to 2022, the year 1961 holds special significance. Wondering why? This is the year the first robotic arm was built and functional in a General Motors facility. Its job was to pick up metal scraps and store them!
Method of operation and elements: Robotics
Since our discussion revolves around Robotics and everything related to it, let us share some details on how they operate and what they consist of.
From the functioning perspective, we have independent and dependent robots. True to their name, independent robots don’t require human intervention to operate. What they need is deep-level programming so that they’re equipped to perform perilous and/or mundane activities, thereby removing the role of humans altogether. Specific examples include bomb diffusion and factory automation. So, while robots are essentially taking the place of human jobs, they’re also making our lives less complicated and time-consuming, and creating opportunities that man couldn’t have imagined was possible earlier.
On the other hand, dependent robots need to communicate with humans to be able to perform their tasks. The technology that goes into such machines is being explored to find more uses for it since it’s a relatively untapped area. We must also add that advanced prosthetics is one aspect that has made substantial progress, and is an area of dependent robots that the human mind controls. Rather fascinating, don’t you think?
While robots are built with varied requirements, there is a set of elements crucial to the making of one, and they include:
- Control system: Comprises the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of the robot and delivers instructions for carrying out parts of a task.
- Sensors: Are nothing more than electric signals that help a robot communicate with the world. Examples would include video cameras (or the eyes), microphones (or the ears), and photoresistors (sensitive to light).
- Actuators: Comprise motor parts that help in a robot’s mobility since a movable body is essential to be considered a robot.
- Power Supply: Comprises the battery that generates the power essential to operate the robot.
- End Effectors: Comprise external features that help a robot complete a job. For instance, surgical robots may carry scalpels while other types of robots might have claws or hands intended to carry out tasks such as packing or deliveries.
Applications: Robotics
As you may have sensed by now, there are limitless possibilities for what Robotics can do and achieve today. In other words, the ideal combination of technology and robots can work wonders across a range of fields and industries. Some prominent instances that come to mind include:
- Robots used at home: While one of the initial home robots was the vacuum cleaner Roomba, a multitude of similar robots have cropped up since then to do a gamut of tasks from mowing lawns to cleaning the stuff we use every day to cleaning swimming pools.
- Robots used for healthcare: It’s incredible how much robots have contributed to the field of healthcare. Besides serving as assistants in surgical procedures, they’ve helped people who sustained injuries, heal through physical therapy. An interesting example is the TUG, a robot that’s entrusted with the task of walking along hospital corridors delivering medicines and related supplies! Finally, robots have, of late, been playing a bigger role in pharmaceutical companies, courtesy of the global pandemic.
- Robots used for transportation: We’d all love a world with vehicles that drive themselves, the only prerequisite being that we sit and enjoy the ride. Thanks to Robotics, we’re not too far away from a future that will have us driving them! Organizations such as Ford, Tesla, and BMW, among others, are working relentlessly to come up with an autonomous vehicle that will require no human intervention at all.
- Robots used in manufacturing: Manufacturing is possibly the very first industry that contributed to the use of robots and cobots (or collaborative robots) for putting together car parts and industrial equipment, not to mention stock stuff. By the way, cobots are a category of robots that work with humans in production processes.
In summary, there are many equally significant instances where we can put robots to good use, such as participating in search and rescue missions when a natural catastrophe takes place, combating forest fires, and helping conserve nature.
Robotics and Relecura
For those of you who may not be familiar with the nature of Relecura’s business, it deals with products, or more appropriately, tools that help resolve innovation and IP-related problems. A blend of these tools can generate extensive and crucial information about new and emerging technologies. Our core patent search and analysis tool, the Enterprise Web Tool, fetches data related to publication (patent) summary, key geographies, key technologies, core application areas, top players (companies), portfolio analysis of top players, emerging companies, etc. concerning a technical area. We’ll explain the nature of the data shared through a few relevant screenshots.
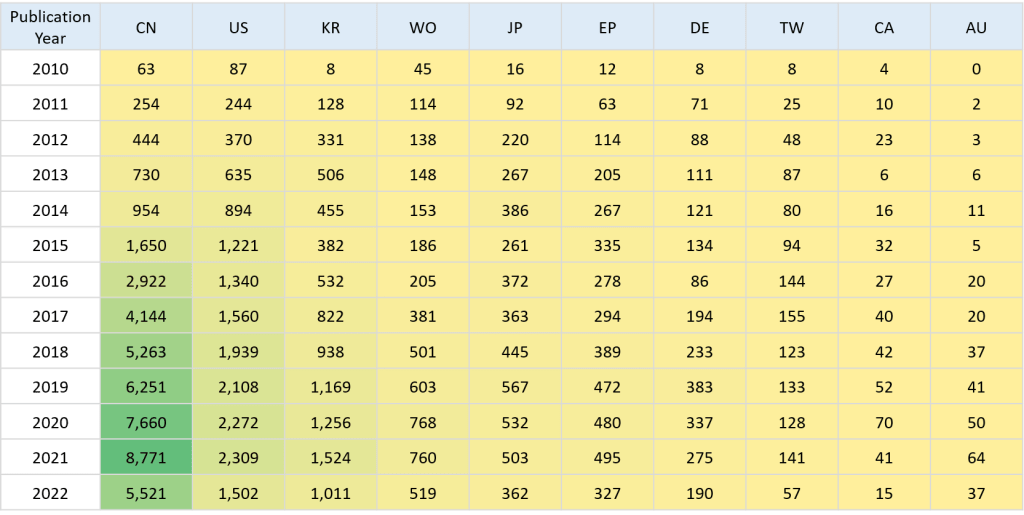
If you are curious about the countries worldwide that have explored Robotics and the patent documents relating to each over a 13-year period, the table below will reveal all the information you need.
If you’re interested in learning about the patent documents concerning core Robotics technologies that were published over 13 years, this table will share the data you need.

Should you need critical findings on the portfolio analysis of the top companies in Robotics, the web tool can generate the relevant information, as revealed in the table below.

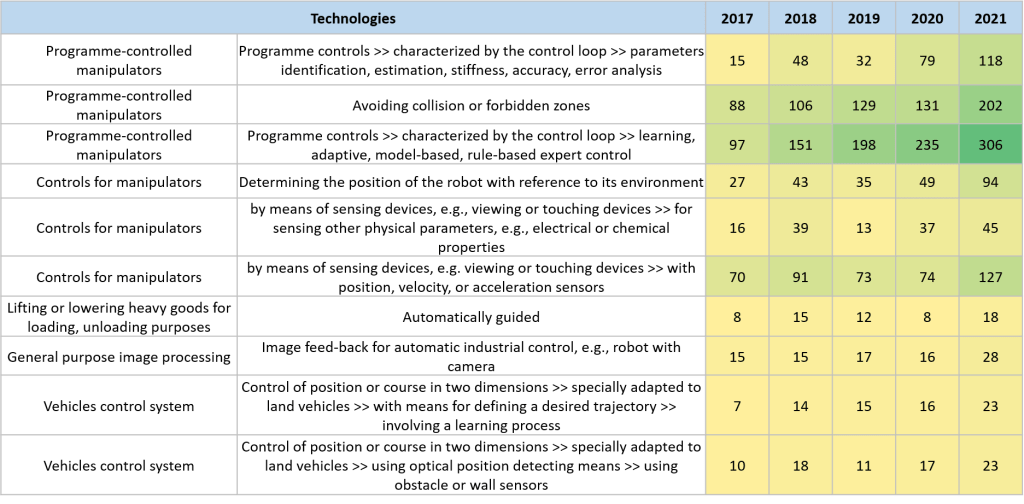
Most of us are aware that Robotics isn’t exactly a new field. Nonetheless, scientists and innovators are far from being exhausted from exploring various facets of it. Robotics technologies that have created a deep impact over a five-year period, are displayed in the table here.
Conclusion
Everything in this universe has a flip side. The field of Robotics is no exception. While we must appreciate the fact that robots have contributed immensely to the lives of human beings in terms of enhancing the safety and accuracy of certain tasks that pose a threat to them, we also need to understand there are areas where robots might never replace humans, and that involves tasks requiring creativity and tough decision-making. In a word, it’s a great idea to continue delving deeper into the technology to find ways to increase its value and usefulness, but it shouldn’t be at the expense of humanity. After all, man is the creator of robots, isn’t he?
Interested in a full report based on Robotics? Please click on the button below:
